Glossary
A to F
🚧 UNDER CONSTRUCTION When users encounter an unfamiliar word, they have access to on-demand audio and text support—a pop-up window with the glossary entry
annual
For one year. The family bought an annual membership to the zoo.
billion
A billion is one thousand millions. It is written as 1 followed by nine zeroes: 1,000,000,000. In 2020,
the world’s population was nearly 8 billion people.
biodiversity
The variety of plant and animal life in a particular place. Biodiversity is nature’s way of keeping things in balance.
census
An official count of people or things in an area. The U.S. Census is taken every ten years.
broad-leaved trees
A family of trees with wide, flat leaves. Oaks and maples are two examples. In cold climates, most broad-leaved trees lose their leaves in fall.
calculate
To determine the exact number or amount of something using math
circle
A closed line that curves around a central point. Every point on the edge of a circle is the same distance from the center.
conifers
A family of trees that have long, thin leaves called needles and produce seed-filled cones. Pines and cedars are two examples. Many conifers keep their leaves all year round.
continent
One of the seven large land
masses on the earth. The seven continents are Asia, Africa,
Europe, North America, South America, Australia, and Antarctica.
data
Information or facts gathered by counting, measuring, questioning, or observing. Data are usually communicated with numbers.
decrease
(verb) To become smaller in size or number
desert
An area of land where very little rain falls. Often sandy with few plants or trees.
estimate
(verb) To make a rough guess about the number or amount of something. (noun) A rough guess about an amount, size, cost, etc.
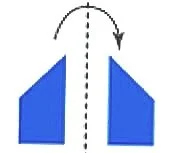
flip
When you flip a shape, you turn it over and see its mirror image.
foot
A unit for measuring height, length, and distance. One foot equals 12 inches and about 30 centimeters.
bar graph
A graph that uses rectangular bars to show how large each value is. A bar graph can have vertical or horizontal bars.
frequency
The number of times a response occurs in a data set
fungi
Living things that release nutrients into the soil by breaking down fallen leaves and dead trees. Mushrooms and molds are examples of fungi.